Useful links
This article explains the idea behind the Recommendation Architect and demonstrates how to use it to design the optimum strategy for any situation.
The Recommendation Architect is a state-of-the-art customization solution that allows you to meticulously craft recommendation strategies that precisely suit your business needs. You can use both static and dynamic scenarios, modify them as necessary, and define how they should work together to deliver the most compelling suggestions to your audience.
A finished strategy can be saved in the Library for future use across the SALESmanago platform. It can also be easily modified based on data insights or changing circumstances.
Adjust your recommendations to the specific characteristics of your audience and specific business goals, to align with your brand strategy, cater to individual needs and preferences, and ultimately drive your sales.
Contents
- Getting started
- Creating a recommendation strategy
- Base scenarios and modifiers
- Example: Creating a recommendation strategy in the Advanced wizard
1. Getting started
Personalized recommendations allow you to deliver highly relevant content and product suggestions to individual customers, and thereby increase engagement and conversion rates. By tailoring offers based on Contact behaviors, preferences, and past interactions, you can enhance the customer experience and foster brand loyalty. By improving personalization efficiency, you can reduce ad spend that might otherwise be wasted on irrelevant audiences. Ultimately, effective personalization drives higher customer satisfaction and revenue growth.
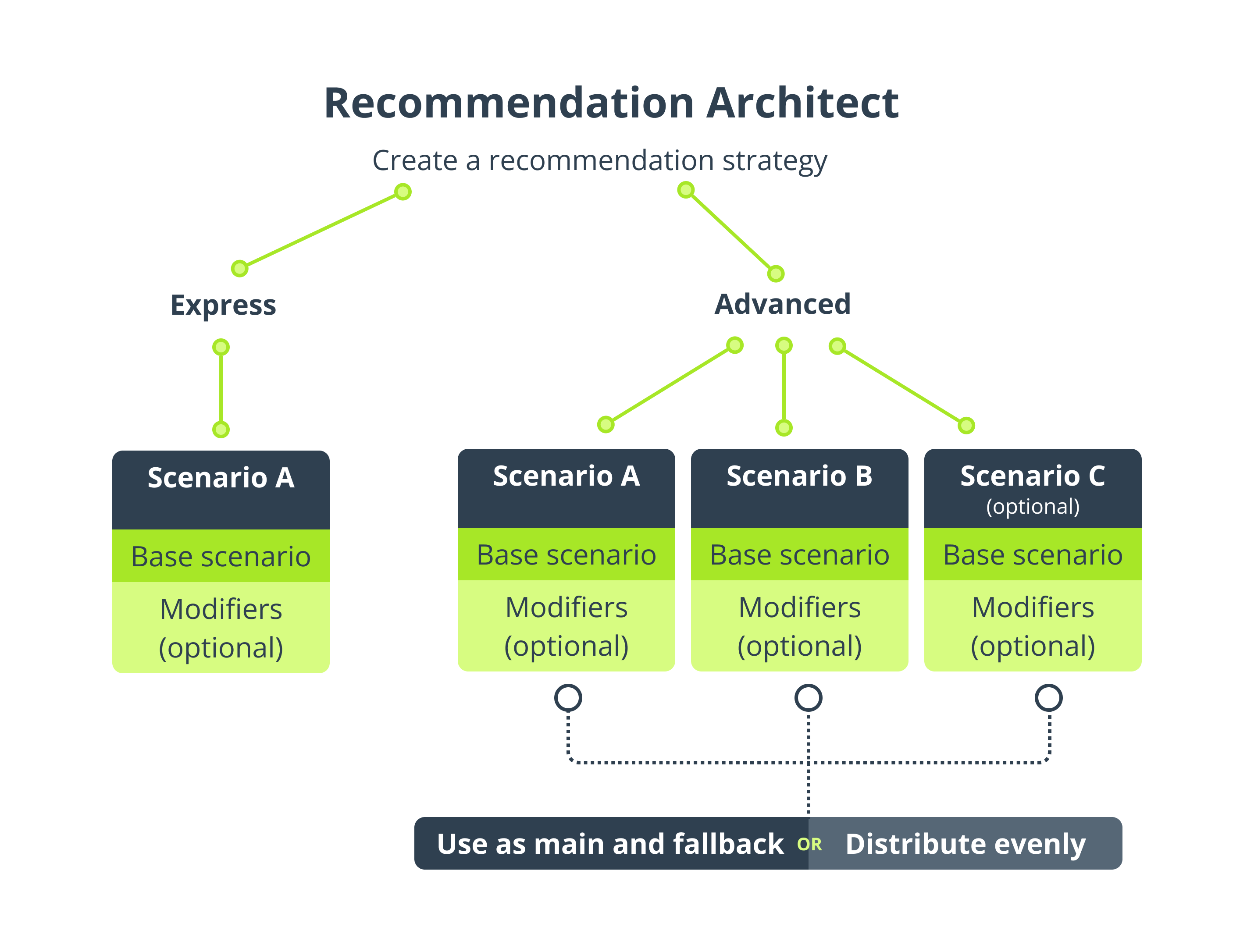
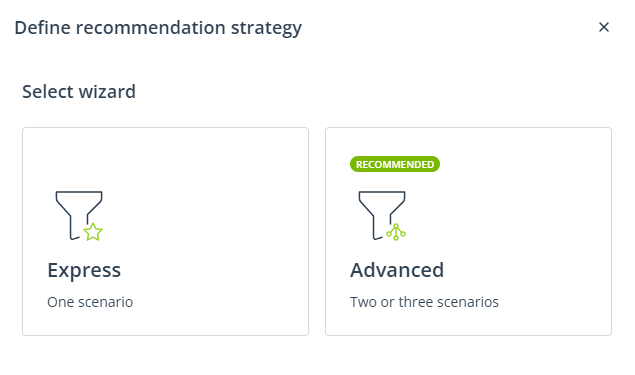
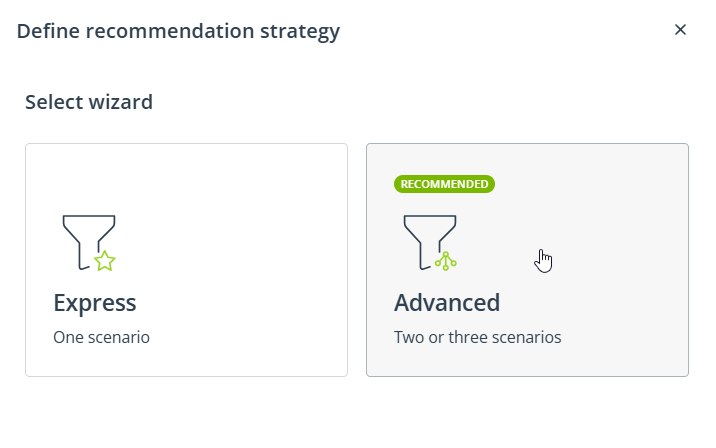
SALESmanago provides a comprehensive solution—the Recommendation Architect—that allows you to tailor your recommendations to the needs of the moment, taking into account the specificity of your business and the products you sell. The tool offers two wizards: Express and Advanced.
When creating a recommendation strategy, first, select one of these wizards.
The Express wizard allows you to create a recommendation strategy consisting of a single scenario. First, you need to select a base scenario from the list. Then, you can apply modifiers to that base scenario.
NOTE: Products matched based on an express strategy are always displayed in a random order (without sorting).
The Advanced wizard allows you to create a recommendation strategy consisting of two or three scenarios (called A, B, and C). For each of those scenarios, first, you need to select a base scenario from the list. Then, you can apply modifiers. Finally, you can specify how Scenarios A, B, and C will complement each other. You can also decide on the product sorting order.
TIP: When devising a strategy for your website, remember to include a scenario that will ensure that some products are displayed to anonymous visitors. For example, if you want to show products left in the cart in a Recommendation Frame, consider using the Advanced wizard and adding a fallback scenario specifically designed for anonymous visitors.
Whether you choose the Express wizard or the Advanced wizard, when your strategy is finished and ready to be implemented, you can also choose whether you want to save it in the Library for future use (read more in Section 2.D below).
Below, you will find further explanations and useful examples that will help you in your work with the Recommendation Architect.
2. Creating a recommendation strategy
When working with the Recommendation Architect, first, you need to choose between the Express and Advanced wizards. Below, you will find instructions for the 4 steps that make up the Advanced wizard. The Express wizard follows a very similar process but includes only 3 steps.
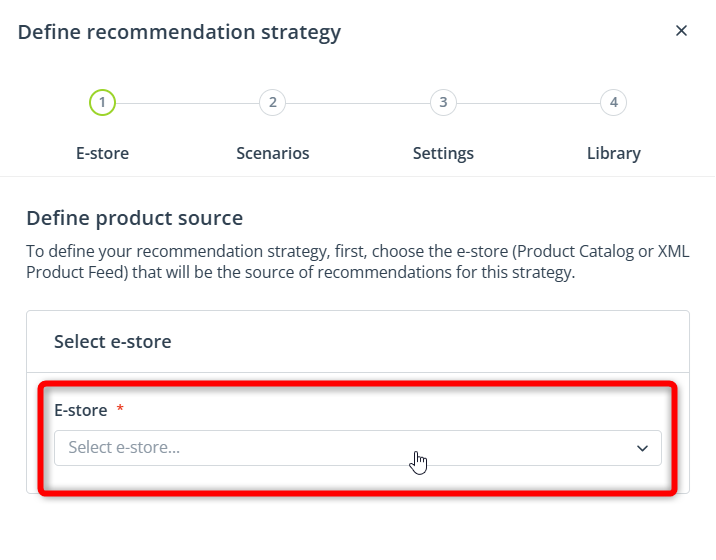
A. E-store
After selecting a wizard (Express or Advanced), choose the e-store (Product Catalog / XML Product Feed) that will serve as the source of your recommendations. The products displayed to your audience based on the recommendation strategy you are going to configure will come specifically from this selected e-store.
Click Next to continue.
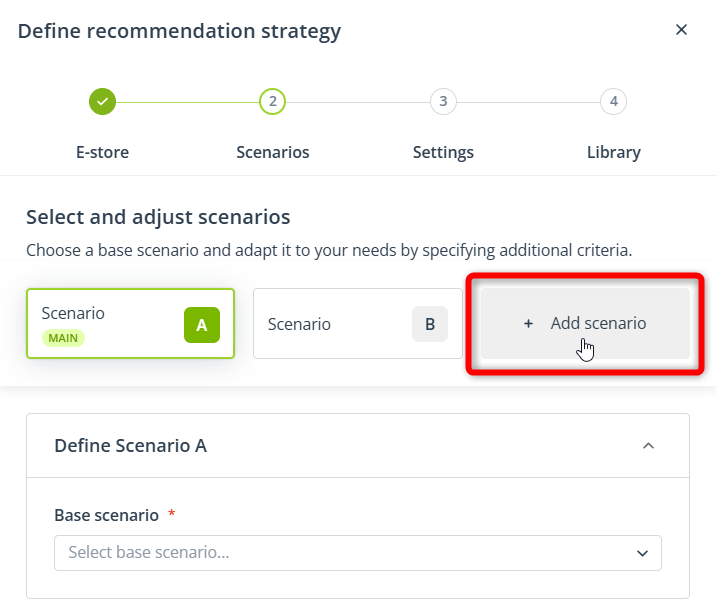
B. Scenario(s)
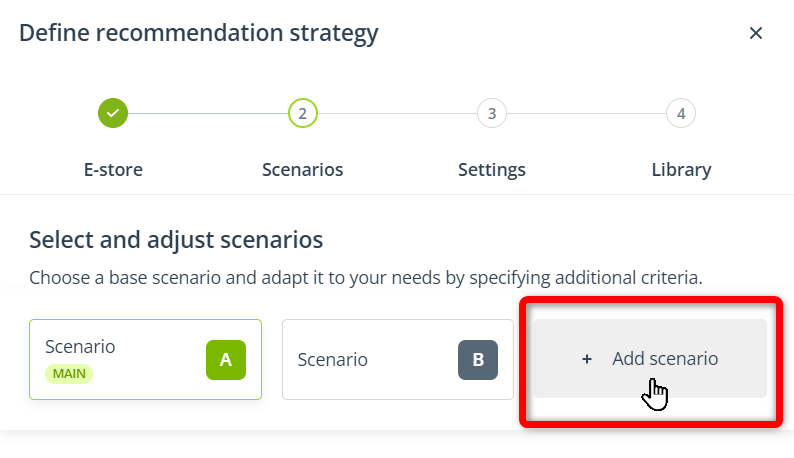
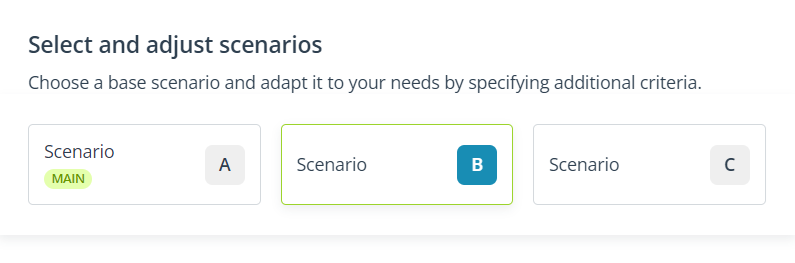
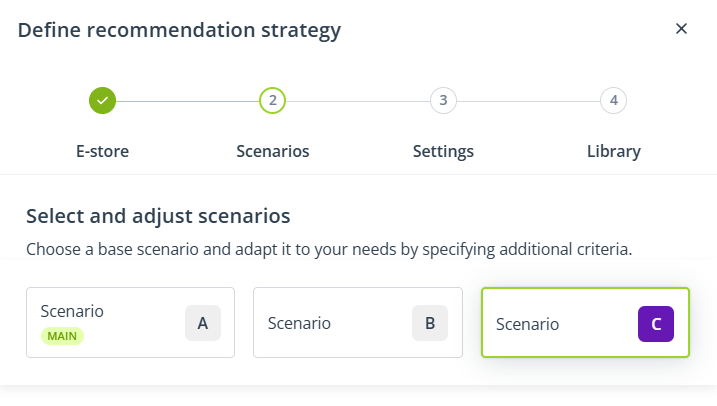
If you are using the Express wizard, in this step, you can configure only 1 scenario. If you are using the Advanced wizard, you can configure 2 or 3 scenarios.
By default, only Scenarios A and B are present. If you want to include 3 scenarios in your recommendation strategy, click Add scenario:
You can switch between these tiles to configure each scenario (A, B, and C) individually:
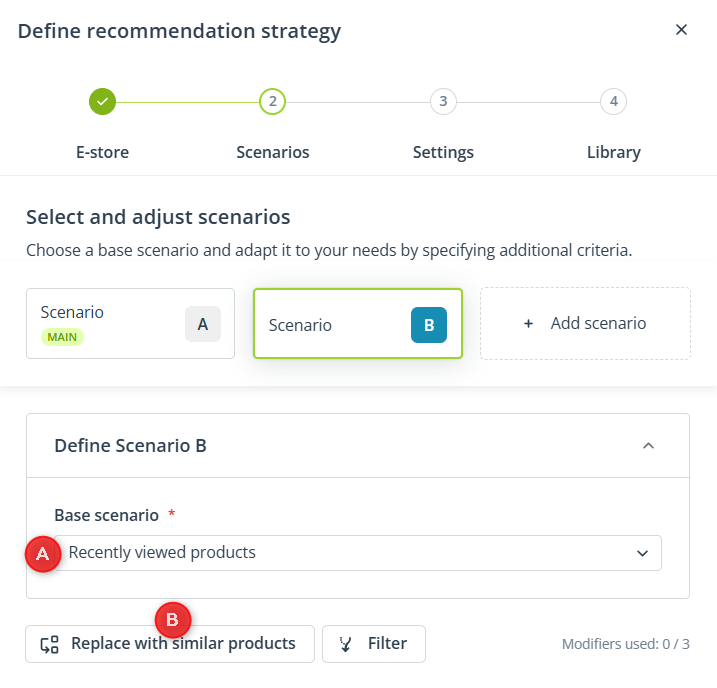
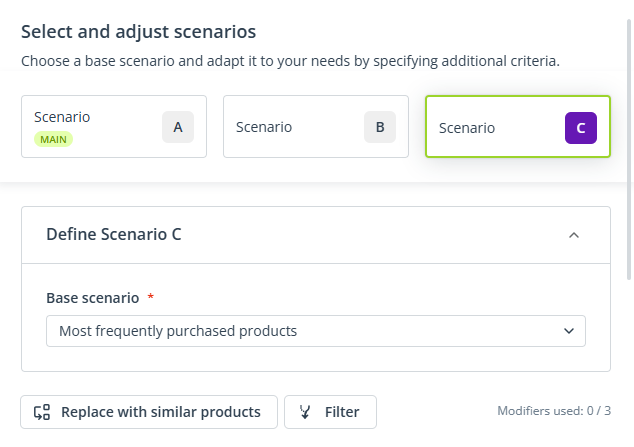
When configuring a scenario (A, B, or C), first, you need to select the base scenario. This base scenario can later be refined using modifiers.
Pay attention to the order in which modifiers are added. Each modifier will be applied to the currently matched products—the set of products resulting from the previous stages of the configuration. If the base scenario is dynamic, the set of “currently matched products” may be different for each Contact, depending on individual data.
EXAMPLE: You choose “Products left in cart” as the base scenario. At this stage, for each Contact, the currently matched products are “those that they left in their carts”.
Next, you apply the modifier: Replace with similar products, based on product detail: color. At this stage, for each Contact, the currently matched products are removed from the recommendations and replaced with the same number of products of the same color. Now, the currently matched products are “products of the same color as those left by Contacts in their carts”.
Finally, you apply the modifier: Filter (Keep products with a popularity score greater than 50). At this stage, for each Contact, all products with a popularity score lower than or equal to 50 are filtered out and excluded. Now, the currently matched products are “products of the same color as those left by Contacts in their carts, having a popularity score greater than 50”.
TIP: Some Contacts may not have the data required for certain scenarios (for example, they may have no products left in the cart or no products in a given Product Collection). For this reason, a recommendation strategy should always include a very general scenario that uses data available for all Contacts (for example, Most frequently purchased products, Products from selected brand, or Products selected manually). In most cases, the recommended practice is to arrange the scenarios from the most specific (and potentially most profitable) to the most general.
In other words, the most specific scenario (requiring individual Contact data) should be set up as Scenario A, the less specific scenario as Scenario B, and the most general scenario as Scenario C.
All base scenarios and modifiers are explained in more detail in this article >>
An example of a strategy configuration is provided in Section 4 below. For further examples and use cases, read this article >>
When you have configured all scenarios (A, B, and potentially C), click Next to proceed to Settings.
C. Settings (Advanced wizard only)
In the Advanced wizard, you can configure a number of additional settings.
Product selection mode
In this section, you can specify how the scenarios configured in the previous step (scenarios A, B, and optionally C) should work together. You can choose between two options:
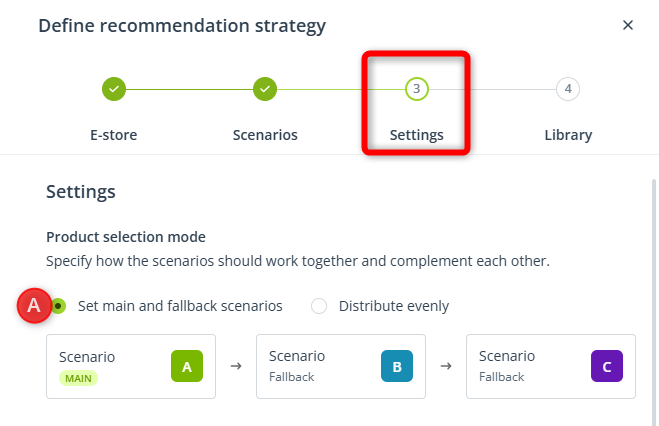
- Set main and fallback scenarios—In this option, you establish a “hierarchy” for your scenarios. Scenario A will be the main scenario, whereas Scenarios B and C will serve as fallback scenarios.
When matching recommendations to individual Contacts, SALESmanago will try to match as many products as possible based on Scenario A. If products selected based on Scenario A are insufficient, the system will resort to Scenario B. If Scenario B does not provide enough products, the system will try to fill any empty spaces based on Scenario C.
EXAMPLE: You create a Recommendation Frame consisting of 10 products. For this Frame, you build a recommendation strategy consisting of the following scenarios:- Scenario A [MAIN]—Products left in cart.
- Scenario B [FALLBACK 1]—Recently viewed products.
- Scenario C [FALLBACK 2]—Products selected manually.
- (For the simplicity of the example, no modifiers are applied to the base scenarios).
A Contact called Jane Doe recently added 3 products to her cart, but did not finalize the purchase. During the same visit, she viewed 5 other products. Now Jane is visiting your website again and the Recommendation Frame is displayed to her.
The Frame has 10 product spaces. SALESmanago starts matching recommendations for Jane based on the main scenario—Scenario A. Only 3 products can be matched on this basis, so the system proceeds to Scenario B and matches 5 further products. The remaining 2 products will be sourced based on Scenario C.
Effect: In this Recommendation Frame, Jane will see the 3 products she left in her cart, the 5 products she recently viewed, and 2 manually selected products.
- Distribute evenly—In this option, all scenarios (A, B, and C) are treated equally.
When matching recommendations to individual Contacts, SALESmanago will try to source an equal number of products from each scenario. If this is impossible, the system will try to match the next product based on Scenario A, then – based on Scenario B, and so on.
EXAMPLE: As in the previous example (for the option: Set main and fallback scenarios), you create a Recommendation Frame consisting of 10 products. You build a recommendation strategy consisting of the following scenarios:- Scenario A [MAIN]—Products left in cart.
- Scenario B [FALLBACK 1]—Recently viewed products.
- Scenario C [FALLBACK 2]—Products selected manually.
- (For the simplicity of the example, no modifiers are applied to the base scenarios).
A Contact called Jane Doe recently added 3 products to her cart, but did not finalize the purchase. During the same visit, she viewed 5 other products. Now Jane is visiting your website again and the Recommendation Frame is displayed to her.
The Frame has 10 product spaces, which should be divided equally among the three scenarios. The SALESmanago system sources 3 products from Scenario A; 3 products from Scenario B; and 3 products from Scenario C. There is 1 product space left. The system tries to fill this space based on Scenario A, however, this scenario provides only 3 products. In this case, the remaining space is filled based on Scenario B.
Effect: In this Recommendation Frame, Jane will see the 3 products she left in her cart, 4 of the products she recently viewed, and 3 manually selected products.
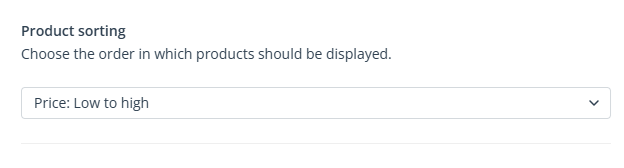
Product sorting
In this section, you can specify how to arrange the products matched to individual recipients. You can choose from a number of options, for example, from cheapest to most expensive, products on discount first, or bestsellers first.
NOTE: Products matched based on an express strategy are always displayed in a random order (without sorting).
You can choose from the following options:
- Price (Low to high/High to low)—The recommended products will be sorted based on the values in the
pricedata field in your e-store. - Discount—Products that have a value in the
discountPricedata field will be displayed first, followed by products for which this field is empty. - Biggest discount—The recommended products will be sorted based on the values in the
priceanddiscountPricedata fields in your e-store. For each product, the system will compare the values in these two data fields and calculate the size of the discount. Products with the highest discounts will be displayed first, followed by products with lower discounts, which in turn may be followed by products with no discount at all. - Most popular—The recommended products will be sorted based on the values in the
popularitydata field in your e-store. - Bestsellers first—Products that have a positive value in the
bestsellerdata field in your e-store will be displayed first. - New products first—Products that have a positive value in the
newProductdata field in your e-store will be displayed first. - Detail 1 to Detail 5 (Low to high/High to low)—The recommended products will be sorted based on the values in the
detailXdata field in your e-store.
You can find some useful sorting tips in the article: Recommendation Architect: Use cases and examples >>
Unavailable products
In this section, you can specify that your recommendations should also include products that are currently unavailable:
Unless you check this box, only available products will be shown in recommendations. Available products are those that have the following values in your e-store (Product Catalog / XML Product Feed): available=true and quantity>0.
When you have defined all the settings, click Next to proceed to the Library step.
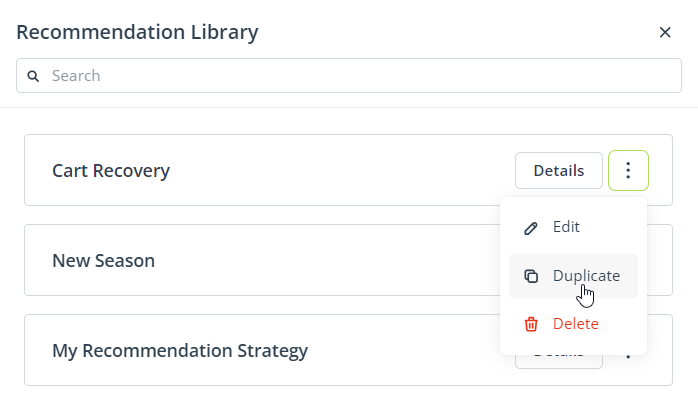
D. Library
Whether you selected the Express wizard or the Advanced wizard, when your recommendation strategy is ready, you can name it [1] and then choose whether you want to save it in the Recommendation Library [2].
A strategy saved in the Library can be re-used in the future—either in the same SALESmanago functionality or elsewhere. For example, a strategy created for a Recommendation Frame can be applied to an email template created in the Email Design Studio.
IMPORTANT: If you edit a strategy saved in the Library, the changes will be applied across the SALESmanago system.
EXAMPLE: You are currently using a strategy called “New Season” in a Recommendation Frame and an email template. When editing the Recommendation Frame, you decide to modify one of the scenarios being part of that strategy. All saved changes will be applied to the email template as well.
The Library provides the option to duplicate a strategy.
With this option, you can create intricate strategies and then easily adjust them for use in other functionalities or for slightly different purposes.
IMPORTANT: If you delete a strategy from the Library, you will no longer be able to apply it in other SALESmanago functionalities (unless you configure it from scratch within those functionalities). However, if the deleted strategy is being used anywhere across the system, it will remain fully functional.
3. Base scenarios and modifiers
When defining a scenario, you can choose from a variety of base scenarios (static, dynamic, and AI-based), which can later be altered and precisely adjusted using modifiers.
You can choose between two modification options:
- Replace with similar products—This modifier substitutes the currently matched products with other products that share the same property or are similar in some respect. As a result, the original (currently matched) products are excluded from the recommendations, and other, similar products are shown instead.
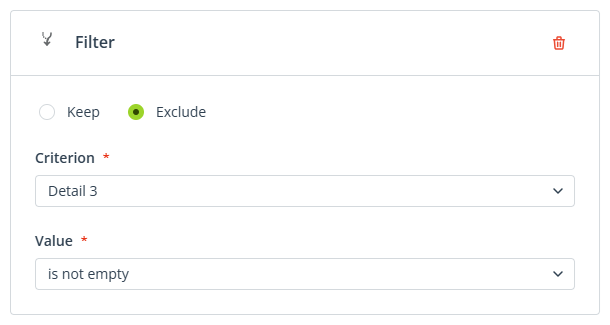
- Filter—This modifier works just like any standard filtering option, except that you can choose between two modes:
- Keep—Specify which products should be kept (included) in the recommendations. Products not meeting the specified criterion will be excluded.
- Exclude—Specify which products should be excluded from the recommendations. Products not meeting the specified criterion will be kept.
All base scenarios and modifiers are described in detail in this article >>
Below is a comprehensive example demonstrating how to create a recommendation strategy based on three scenarios, each of which includes modifiers.
4. Example: Creating a recommendation strategy in the Advanced wizard
Below, you will find step-by-step instructions for configuring an advanced strategy for a Recommendation Frame. The strategy consists of three scenarios:
- Scenario A [MAIN]. Recently viewed products that are currently discounted.
- Scenario B [FALLBACK]. Products from the same main category and for the same gender as those recently viewed.
- Scenario C [FALLBACK]. Most frequently purchased products.
Product selection mode: Set main and fallback scenarios
Product sorting: Price: Low to high
With this strategy, you aim to convince Contacts who are already interested in some products to actually purchase these or similar products. Scenario C, however, is a typical “fallback” scenario, intended to fill all product spaces that could not be filled based on Scenarios A and B.
To create this strategy:
1. Go to the Recommendation Architect and select the Advanced wizard.
2. In Step 1: E-store, select the Product Catalog or XML Product Feed from which you want to source product data.
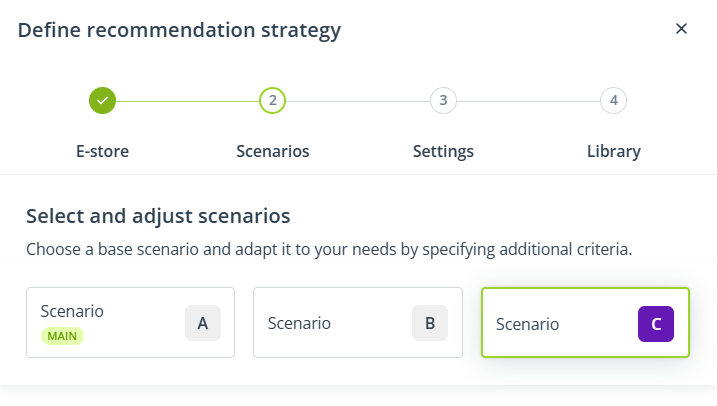
3. In Step 2: Scenarios, start by clicking Add scenario (because you want to create a strategy made up of 3 scenarios).
Scenario C will be added:
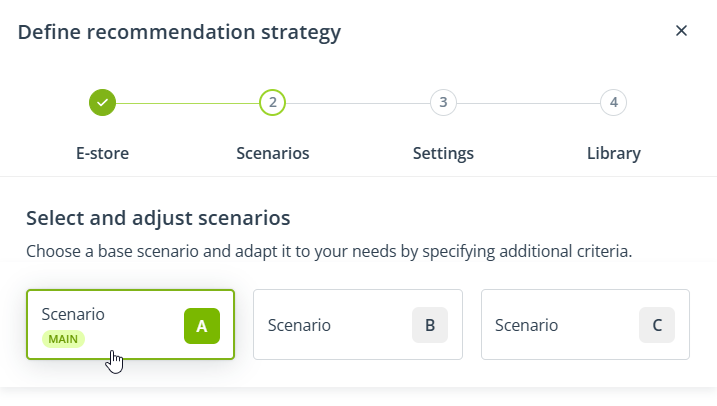
Return to the tab: Scenario A, to start configuring the strategy from this scenario.
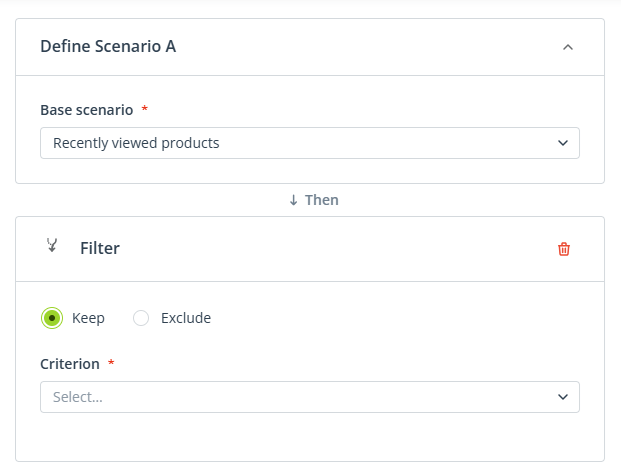
4. Configure Scenario A: Recently viewed products that are currently discounted.
First, select the base scenario: Recently viewed products.
Then, modify the scenario to include only products that are currently discounted.
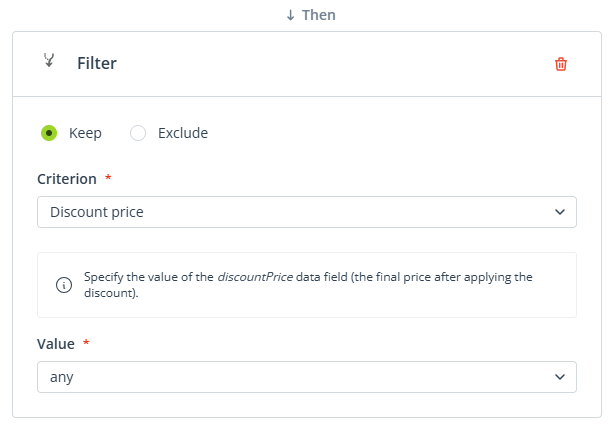
Add the modifier: Filter and select the option: Keep.
Select Discount price as the criterion. You want to show any products that are currently discounted, so select any as the value.
detail3 data field. You can filter out any variants from your recommendations with the following configuration:
Now, if a Contact views a blouse (parent product) in multiple colors (variants), only the parent product (base color) will appear in their recommendations. This way, all product spaces will contain different products.
In this example (Scenario A), this filter could be applied either before or after the other modifier (in this example: Filter – Keep – Discount price – Any) without impacting the final outcome. However, in most cases (especially in combination with the modifier: Replace with similar products), this specific exclusion should be added as the last modifier.
Scenario A is now fully configured. You can switch to the next tab: Scenario B.
5. Configure Scenario B: Products from the same direct category and for the same gender as those recently viewed.
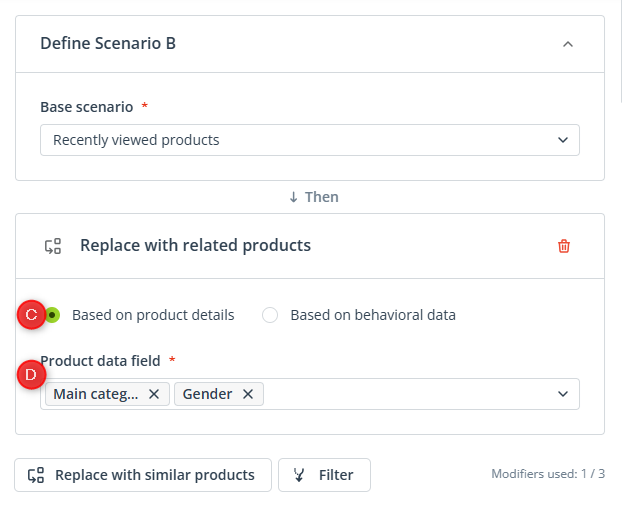
First, select the base scenario: Recently viewed products [A]. Next, add the modifier: Replace with similar products [B].
Now, configure the modifier. Choose the option: Based on product details [C].
Now, select the Product data fields [D] based on which you want to match recommendations: Main category and Gender.
Scenario B is now fully configured. You can switch to the next tab: Scenario C.
6. Configure Scenario C: Most frequently purchased products.
Select the base scenario: Most frequently purchased products.
You want this scenario to be as general as possible, so you decide not to apply any modifiers.
All scenarios are now fully configured. Click Next to go to Step 3: Settings.
7. Configure the settings for your recommendation strategy.
Start from the Product Selection Mode. Here, you need to decide how the scenarios will work together. You want to source as many products as possible based on Scenario A, so you select the option: Set main and fallback scenarios [A].
With this configuration, SALESmanago will try to source as many products as possible from Scenario A. If any product spaces are left empty, Scenario B will be used, and only then Scenario C.
Then, proceed to the Product sorting section. You want to show products from the cheapest to the most expensive, so select the appropriate option from the list:
Finally, you can choose whether you want to include currently unavailable products in your recommendations. For this strategy, you decide to leave this checkbox empty:
All Settings are now configured. Click Next to proceed to Step 4: Library, where you can choose whether you want to save this new strategy for future use across the SALESmanago system.
Finally, click Finish to actually save the strategy.
You will find further examples and inspirations in the article: Recommendation Architect | Use cases and examples >>